An Overview of Transformers in Landscape Lighting
The Enlightening World of Landscape Lighting
Landscape lighting, an often overlooked aspect of home decor and outdoor aesthetics, plays an indispensable role in enhancing the beauty, safety, and functionality of our outdoor spaces. It involves the strategic placement of light fixtures throughout your garden, lawn, or yard to not only illuminate the area but also highlight specific features such as trees, shrubs, or architectural details. These lights create an enchanting ambiance after sunset and increase visibility in areas that would otherwise be masked by darkness.
While some may perceive landscape lighting as mere decorative fixtures strategically scattered across yards or gardens, it is a meticulously planned process that entails understanding the interplay between light and shadow. The magic lies not just in highlighting key focal points but also in creating a harmonious balance between lit and unlit areas.
This delicate equilibrium can transform a mundane outdoor space into a magical wonderland that invites curiosity and admiration alike. The range of landscape lighting is extensive; from path lights that guide your steps along walkways to floodlights that bathe walls with a wash of light; from accent lights that spotlight distinctive features to water lights that add shimmering reflections on ponds – each one serves a purpose while adding its own unique charm.
The Enlightened Placement: More Than Meets the Eye
When it comes to landscape lighting, one must understand the significant impact proper placement has on achieving optimal results. Proper placement ensures efficient use of electrical energy while maximizing aesthetic appeal and functional benefits.
Firstly, strategic positioning enhances the visual appeal of your landscape architecture by focusing on architectural features or natural elements you wish to showcase – be it majestic trees, charming footpaths, or fascinating water bodies. Thus, well-placed lights can transform ordinary landscapes into extraordinary vistas teeming with life after dark.
A thoughtfully designed lighting layout enhances security by illuminating dark corners prone to trespassing or accidents. By casting wide beams over driveways, entrances, and walkways, it ensures safe navigation for guests while deterring potential trespassers.
Moreover, an effective lighting plan can define the purpose of specific outdoor areas. For instance, brighter lighting in alfresco dining areas or barbecue pits encourages social interactions, while softer, diffused lights around seating arrangements create a tranquil atmosphere conducive to relaxation.
Adequate lighting placement is critical to maintaining the health of your flowers. Positioning lights too close may increase heat exposure, affecting plant growth and longevity; conversely, placing them too far might not provide enough light for showcasing your garden’s prized possessions.
Transforming Landscapes: The Power Behind Your Lights
The silent workhorse behind every successful landscape lighting design is the transformer – an electrical device that regulates voltage supply to your light fixtures. Transformers are crucial in landscape lighting as they convert high-voltage household current (usually 120 volts) into a lower voltage (typically 12–15 volts) suitable for outdoor fixtures. This makes landscape lighting safer and prevents any possible hazards that could occur due to water exposure or accidental contact with live wires.
Apart from safety considerations, transformers also extend the lifespan of your lights by reducing electrical stress on bulbs, thereby ensuring consistent brightness despite fluctuations in main supply voltage and preventing premature burnouts. Moreover, most transformers come with timers or photocells, allowing automated operations based on user preferences or natural light cycles, thus offering convenience while conserving energy consumption.
Understanding transformer capacity is crucial when designing your landscape lighting layout. A transformer’s capacity determines how many lights it can support and how far apart they can be installed – factors pivotal in creating a balanced and efficient lighting plan.
Understanding Transformers in Landscape Lighting
The Quintessence of Transformers
A transformer, in its most basic definition, is a device that modifies the voltage of an electric current. In a landscape lighting context, transformers serve as the heart of low-voltage lighting systems, converting high-voltage electricity from your main power supply to a safer, more manageable 12V or 24V current suitable for outdoor lights. This change in voltage allows for energy-efficient operation and greatly minimizes potential electrical hazards.
In essence, a transformer operates on two principles: electromagnetic induction and Faraday’s Law. It consists of two or more coils termed ‘windings’. These windings are enveloped around the core, which induces a magnetic flux. The primary winding receives the input voltage, while the secondary winding delivers the output voltage through an interaction of magnetic fields.
A Closer Look at Landscape Lighting Transformers
Transformers utilized for landscape lighting purposes can be grouped into three broad categories: electronic low-voltage (ELV) transformers, magnetic low-voltage (MLV) transformers, and digital transformers. ELV transformers are compact and lightweight but may exhibit humming noises when operating under heavy loads or when used with incompatible dimmers.

MLV transformers are generally larger and silent but may not be compatible with modern LED bulbs due to their minimum load requirements. Digital transformers have become increasingly popular due to their compatibility with both older halogen bulbs and newer LED technology. They also offer additional features such as built-in timers and photocells for automatic sunset/sunrise detection.
Deciphering the Right Transformer Choice
The choice of transformer is influenced by several factors: the total wattage requirement of your lighting setup, compatibility with bulb technology (LED vs incandescent), desired features (timer functionality, photocell integration), environmental conditions (weather exposure), budget constraints, and even aesthetic considerations.
The total wattage requirement is calculated by adding up the individual wattages of all lights in the system. This sum should not exceed 80% of the transformer’s maximum load for optimum performance and longevity. The compatibility of transformers with bulb technology requires careful understanding and examination to prevent flickering issues or premature bulb failure.
Further Considerations on Transformer Selection
Desired features such as built-in timers or photocell integration can offer convenience and energy-saving opportunities. Environmental conditions play a role as well, with transformers housed in weather-resistant enclosures being more suitable for outdoor exposure.
Your budget and aesthetic considerations are also crucial; while higher-end models promise advanced features and sleek designs, a basic model may suffice for simpler lighting setups. Understanding the function of transformers in landscape lighting and making an informed choice based on several influencing factors is vital to creating an efficient, safe, and visually pleasing outdoor space.
A Journey of a Thousand Lumens: The Basics of Distance Between Transformers and Landscape Lights
In the realm of landscape lighting, pondering about the optimal distance between transformers and lights is not a frivolous pursuit. Rather, it is an essential aspect that can greatly impact the overall performance and longevity of your lighting system.
The general rule for positioning landscape lights relative to their power source – the transformer – hinders profoundly on the power capacity of your transformer, combined wattage of all the lights, wire size, as well as wire length or the physical distance to be covered.
The fundamental precept in determining this distance is maintaining an optimal balance to avoid overloading your transformer while also ensuring that each light fixture gets adequate voltage supply. A guideline often recommended by professionals is keeping this distance within 100 feet for systems deploying 12-gauge cable and a total load not exceeding 200 watts.
Within this context, it’s important to understand that transformers are typically placed close to the main power source (usually near a building or house), while landscape lights are scattered across different parts of your yard or garden, which may entail covering considerable distances. Thus, while planning your installation, you should ensure that no light fixture positioned furthest from the transformer exceeds this 100-foot guideline.
However, do take cognizance that this rule isn’t sacrosanct and may need deviation based on specific requirements or restrictions posed by your landscape’s topology and features. For instance, if you have a larger garden with numerous light fixtures at varying distances from each other necessitating extensive wiring, you might need to consider using heavier gauge cables or employing multiple transformers.
The Voltage Drop Enigma: Unraveling its Impact
Diving deeper into our luminary journey brings us face-to-face with a somewhat arcane yet critical term in electrical engineering parlance – voltage drop. Understanding this concept is pivotal because it significantly affects the overall performance, efficiency, and longevity of your landscape lighting. In simple terms, voltage drop refers to the reduction in electrical potential as it travels along the length of a wire.
In the case of landscape lighting, it implies the decrease in voltage that occurs as electricity traverses from your transformer across the length of wiring to reach each light fixture. This reduction happens due to resistance encountered by electricity as it flows through wires and connectors.
The longer the distance covered or higher the load (total wattage connected), the more pronounced this drop becomes, often leading to suboptimal performance or even damage to light fixtures. For instance, if you have a 12-volt system and your furthest light receives only 9 volts due to a significant voltage drop, it may result in dimmed lighting or flickering.
Prolonged supply of low voltage can even reduce the lifespans of bulbs or cause permanent damage. Therefore, calculating and mitigating voltage drop is an integral part of the planning and installation process for landscape lights. It guides decisions like appropriate transformer capacity, cable size selection, and layout design, among others – all aimed at ensuring every single light fixture shines bright with optimal brilliance.
To sum up our lighting journey, bear in mind that understanding how far from a transformer you can install landscape lights doesn’t just enhance aesthetic appeal but also safeguards your investment, ensuring every corner of your landscape is aglow with reliable luminosity.
The Exigencies that Influence Installation Distances
A Deep Dive into the Power Capacity of Transformers
The power capacity of a transformer, quantified in watts, dictates its ability to sustain the electrical requirements of multiple landscape lights. It is a fundamental rule that the collective wattage of your landscape lights must not exceed the power capacity of your transformer. This crucial balance ensures optimal functioning and longevity of both your lights and transformer.
Understanding this principle requires acknowledging the nature of electrical energy. Electricity flows like water, subject to pressure (voltage) and its path’s width (amperage). The total amount flowing, analogous to water’s volume, is power measured in watts. Thus, if a fountain requires more water than a pipeline can provide (overloading), it affects both the fountain’s operation and potentially damages the pipeline.
Consider an example: If you own a 200-watt transformer, ensure that when all connected landscape lights are lit simultaneously, they do not draw more than 200 watts in total. A higher demand could lead to premature failure or suboptimal lighting conditions due to an overburdened transformer.
How Total Wattage of Lights Plays Its Part
In conjunction with your transformer’s capacity is another pivotal factor – total wattage drawn by all lighting fixtures combined. One might wonder why we can’t just use one powerful light for our entire garden instead of many smaller ones scattered throughout. Well, light distribution matters just as much as light intensity when it comes to landscaping aesthetics.
Every light fixture has its wattage rating, which determines how much electricity it consumes to produce bright illumination. By adding up these individual ratings while planning your landscape lighting setup, you ensure you don’t exceed your transformer’s limit but also allow for efficient distribution across lengthy distances without voltage drop issues – an important factor considered in our next section.
The Intricate Dynamics of Wire Size and Its Impact on Distance
The size or gauge of the wire connecting your lights to the transformer plays a significant role in determining the maximum distance your landscape lights can be installed from the transformer. This is due to a phenomenon known as voltage drop, which refers to the decrease in electrical potential as electricity travels along a wire.
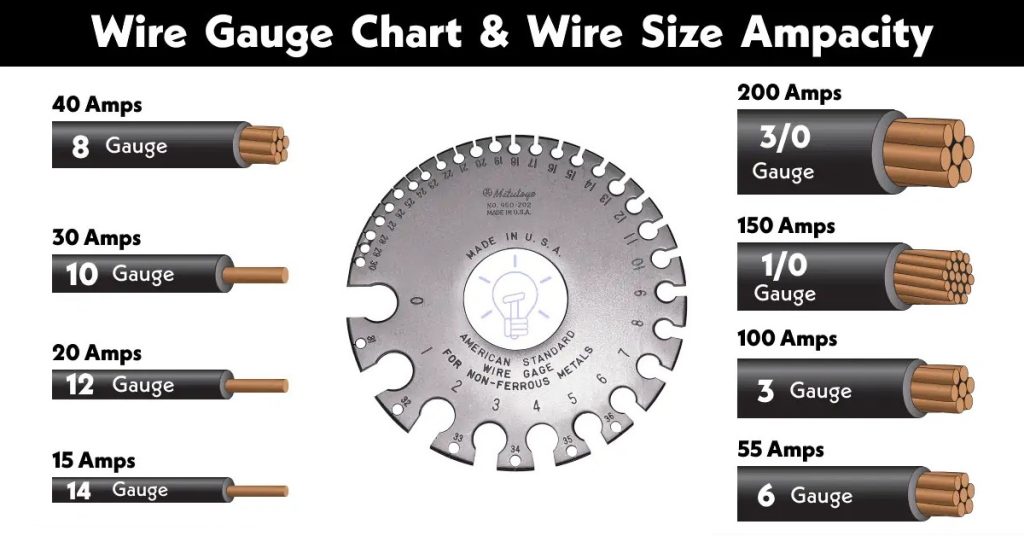
A thicker wire (lower gauge number) offers less resistance to flowing electric current, thus reducing voltage drop over long distances. Conversely, a thinner wire (higher gauge number) introduces more resistance and increases voltage drop. Therefore, if your landscape design requires distant light placements from your transformer, using thicker wires becomes requisite.
Understanding Voltage Rating and Its Effect on Installation Distance
Voltage rating is another fundamental element defining how far you can place your lights from their power source. Landscape lighting systems typically come in low-voltage variants, commonly 12V or 24V, due to safety measures and energy efficiency. However, higher voltage systems can effectively mitigate voltage drop issues over longer runs.
For instance, a 24V system will lose less voltage over the same distance compared with a 12V system when using identical wiring. So if you plan for extensive lighting coverage throughout large areas requiring greater distances between lights and transformers, considering higher-rated voltage systems might make sense.
The Role of Landscape Features in Influencing Installation Distance
Last but not least are physical features within your landscape that may influence installation distance. These include natural barriers like trees or rocks that might necessitate winding paths for wiring, desiring longer wires than direct lines would require.
Additionally, physical elements such as bodies of water or terrains with varying elevation levels could also impact installation strategies. Arrangements demanding underwater lighting fixtures or those installed at significant heights would require dedicated considerations about optimal positioning relative to transformers – an art more than mere technicality ensuring both aesthetic appeal and efficient power utilization.
Deciphering the Optimal Distance for Installation
A Step-by-Step Guide to Calculate Optimal Distance
Calculating the optimal distance between your transformer and landscape lights involves a bit of arithmetic, but don’t worry, it’s simple. Let’s assume you’re using a 12V system. First Step: begin by identifying your transformer’s capacity (in watts) and the total wattage of all lights you intend to install.
Second Step: ascertain the wire size you’ll use, remembering that thicker wires can accommodate more power over longer distances with less voltage drop. Third Step: With these variables in hand, consult manufacturer-provided tables or online calculators designed for plotting landscape lighting layouts. These tools factor in both power demand and cable gauge to provide an estimated safe maximum distance from light fixtures to transformers, ensuring adequate voltage supply and avoiding the ill effects of excessive voltage drops.
Pro Tips To Minimize Voltage Drop
Voltage drop is an inevitable yet manageable aspect of landscape lighting design. Several strategies can help minimize its impact on your lighting quality. First, opt for parallel circuitry instead of daisy-chaining your light fixtures; this configuration ensures each light draws power directly from the transformer rather than depending on preceding lights.
Next, consider installing multiple transformers if feasible; dividing the total lighting load among them reduces individual transformer stress while also enabling closer proximity to distant lights, minimizing wire length and hence voltage losses. Remember, efficiency is a virtue here; use LED bulbs that produce bright lighting at significantly lower wattage demands, easing the burden on both transformers and wiring networks altogether and ensuring consistent brightness across all fixtures irrespective of their distances from power sources.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications
Navigating a Large Garden with Multiple Light Fixtures
Consider Mr. GreenThumb, who has a sprawling garden adorned by 20 landscape lights. Each light has a wattage of 10 watts, totaling 200 watts. His transformer’s capacity is also 200 watts – perfect match! But his garden’s vast expanse necessitates some lights to be installed far from the transformer. Here’s how he smartly negotiates this situation.
Mr. GreenThumb uses thick (12-gauge) wires, reducing resistance and hence voltage drops, ensuring all far-off lights receive adequate power supply for bright illumination. Furthermore, he adopts a parallel wiring configuration, facilitating each light to draw direct power supply from the transformer instead of depending on power left over by preceding fixtures in the line – an intelligent approach satisfying both aesthetics and technicalities.
Lighting Up a Small Backyard with Fewer Light Fixtures
Meet Mrs. Dainty, who owns a small but cozy backyard that she wants to light up using four landscape lights each rated at 20 watts, and her transformer carries a capacity of 100 watts – more than sufficient for her lighting needs! Her primary challenge is not distance or wattage, but how best she can highlight key elements like her barbeque area or that old oak tree within this limited space.
Mrs. Dainty skillfully places her lights such that they cover these features without causing excessive glare or shadowy areas while keeping wiring hidden as much as possible, maintaining aesthetics intact. She uses thinner wires (16-gauge) as distance from transformers isn’t an issue, saving costs while enjoying beautiful lighting just at the right intensities where required.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Installing Landscape Lights Near Transformers
Avoid Overloading your Transformer
The absolute first rule when planning your landscape lighting setup is never overload your transformer; its capacity in wattage must equal or exceed the total wattage of all connected fixtures; otherwise, it could lead to suboptimal brightness levels due to insufficient voltage supply or even damage your transformer with overheating issues. Remember, balance is key here.
If you require more lights than your current transformer can handle, consider adding another transformer to share the load. This ensures the longevity of all components while promoting better lighting quality across all fixtures.
Don’t Neglect Voltage Drop
Ignoring voltage drop is like forgetting the sugar while baking a cake – it just won’t turn out right. A voltage drop can lead to dim lighting or even light failure if not properly addressed.
It is particularly crucial for larger gardens where lights are placed at great distances from the transformer. Mitigating voltage drop involves choosing the correct wire gauge, employing parallel wiring configuration, and considering higher voltage systems for longer runs if necessary. Remember, proper planning in this regard will save both time and resources while ensuring optimal brightness levels throughout your beautiful landscape.
Never Ignore Wire Size
Wire size may seem trivial against factors like wattage or distance, but its role in shaping an efficient landscape lighting setup is indispensable. Thicker wires carry electricity over long distances more effectively, reducing associated voltage drops, while thinner wires are economical choices for compact spaces where light fixtures reside close to transformers. Choosing an appropriate wire size not only facilitates bright and consistent lighting but also adds safety measures against potential electrical hazards due to overheating on account of excessive resistance from inadequate wire thickness – so never sideline this critical aspect of your landscape lighting setup!
Advanced Techniques for Extending Installation Distance
Leveraging Multiple Transformers
A single powerful transformer could indeed power many lights but might fall short when spanning large areas due to inherent limitations on how far it can effectively deliver power without significant voltage drops affecting brightness levels adversely.
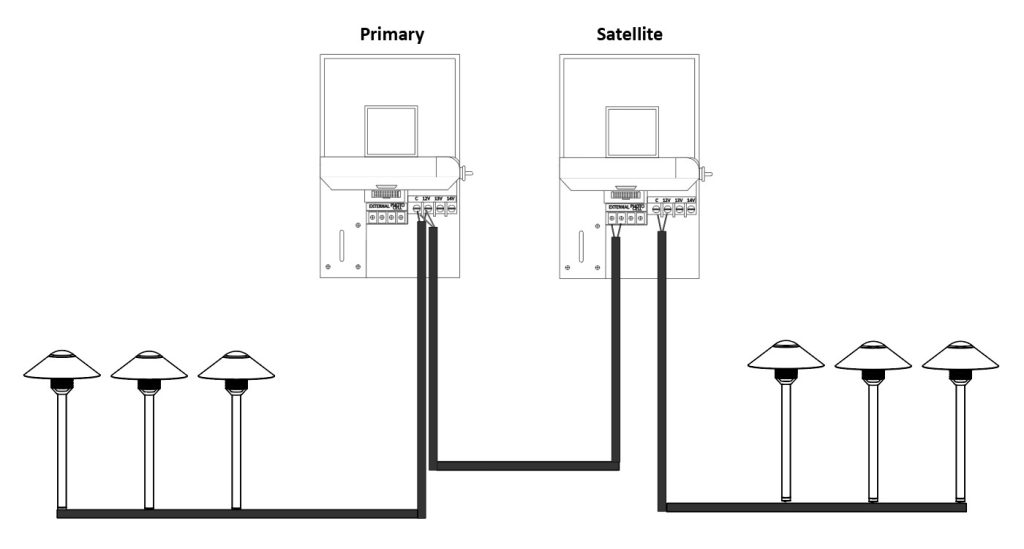
This scenario calls for deploying multiple transformers across different zones within your garden, each catering to proximal fixtures, thus overcoming distance-related challenges and improving overall illumination quality significantly.
Choosing LED Bulbs to Reduce Wattage Demand
LED bulbs are a game-changer in landscape lighting. They consume significantly less power (less wattage) than traditional bulbs for the same brightness levels. This means you can use more LED lights without overloading your transformer.
Moreover, LEDs produce very little heat and have a longer lifespan compared to their traditional counterparts. This translates into cost savings in the long run from reduced energy bills and infrequent bulb replacements, making them an attractive choice for persons seeking both utility and economy in their landscape lighting ventures.
Opting for Higher Voltage Systems
The higher the voltage, the less current is required to carry the same power, which minimizes energy loss over long wire runs. This allows lights to maintain consistent brightness, even at extended distances from the transformer.
A higher voltage system is especially useful for large properties, complex layouts, or installations that involve multiple lighting zones spread across significant distances. In these cases, a 24V system or even higher-voltage options may be the optimal choice to ensure efficient, reliable operation. Furthermore, using thicker gauge wire, such as 10 or 12 gauge, in combination with a higher voltage, can further mitigate voltage drop issues.
Strategic Placement Techniques
Strategic placement techniques also play a big part in mitigating voltage drops. Placing the lights closer together, in relatively close proximity to the transformer, or using thicker wire for longer distances are worthy considerations.
Conclusion: How Far From the Transformer Can Landscape Lights Be Installed?
It’s evident that numerous factors determine how far from the transformer landscape lights can be installed. Proper planning and precise calculations regarding voltage drop, wire size, and total wattage load are crucial elements shaping this decision. With this newfound knowledge at your disposal, may every nook and cranny of your landscape bathe beautifully under strategically placed luminance that not only enhances aesthetic appeal but also contributes to safety and visibility in outdoor spaces at night.
You may also be interested in the following posts:
