Scientific Findings about LED Strip Lights and Heat Generation
The Quest for Lighting: An Exploration of LED Strip Lights
LED strip lights, also known as tape lights or ribbon lights, have revolutionized the world of lighting with their versatility and energy efficiency. They are long, flexible circuits populated with tiny light-emitting diodes spaced at regular intervals.
These LEDs emit a bright but diffused light that makes them ideal for both decorative and functional purposes. The ease of installation and low power consumption make LED strip lights a modern marvel in lighting technology. Available in a broad spectrum of colors and being highly customizable, these luminous strips find utility in countless applications.
With the advent of landscape strip lights, even our outdoor spaces are not left untouched by their radiant charm. Landscape lighting has been wonderfully transformed due to these adaptable light strips, turning gardens into nocturnal wonderlands.
Despite their compact size, these small beacons of light are incredibly potent when it comes to brightness and coverage. From accentuating architectural features to adding a dash of drama to interior spaces or illuminating hard-to-reach spots, LED strip lights have proven themselves indispensable in all kinds of lighting scenarios.
However, not many realize that this impressive versatility is owed as much to the design as it is to the technology behind these light sources. In essence, understanding what goes on behind this radiating brilliance is crucial for fully appreciating the potential packed within each slender strand.
The functionality and lifespan of LED strip lights hang significantly upon one critical factor – heat generation. This seemingly minor aspect plays an enormous role in determining how well your LED strip performs over time. Therefore, it’s essential that we delve into an exploration regarding if and how much heat these luminous tapestries actually generate.
Fanning the Flames of Knowledge: Why Understanding Heat Generation Matters
An often overlooked aspect of LED strip lights is their heat output. The common misconception is that LEDs do not produce heat. However, like any electronic device, they do generate some amount of heat during the lighting process. This fact does not diminish their superiority over traditional lighting systems but reinforces the importance of understanding their thermal characteristics.
Despite being more energy-efficient than traditional incandescent or CFLs, LEDs can still suffer from issues related to overheating. Excessive heat can shorten the lifespan of your LED strip lights and decrease their efficiency over time.
Understanding how much heat these ingenious sources of light produce can help you make informed decisions about where to install them and how to manage any heat they do generate. A cool-running LED strip light will offer more consistent performance and longer life. In landscape lighting scenarios, knowing how much heat your LED strip lights are likely to generate can dictate installation locations and types.
For outdoor installations in particular, considerations like environmental temperature fluctuations become crucial in maintaining optimal performance. In essence, delving into the thermal characteristics of LED strip lights isn’t simply an academic exercise; it’s a practical necessity for those seeking to enjoy the benefits of this versatile form of lighting for years to come.
Unraveling the Glow: What Are LED Strip Lights?
LED strip lights – a term frequently bandied about in conversations related to lighting, decor, and technology. But what exactly are they? LED strip lights are flexible circuit boards populated with numerous tiny light-emitting diodes (LEDs) that give off light when a current is applied. They come in varying lengths, can be cut according to specific needs, and are typically adhesive-backed for easy installation.
While being a marvel of modern technology, these lights encapsulate simplicity and versatility. They are composed of three key components: a printed circuit board (PCB), surface-mounted device light-emitting diodes (SMD LEDs), and resistors that control the current flow, safeguarding the longevity of each individual LED. The fusion of these elements crafts not just an impressive light source but an innovative solution for various lighting needs.
Their sleek form factor allows them to be installed virtually anywhere without disrupting aesthetics – behind television units, under kitchen cabinets, inside wardrobes; the possibilities are almost boundless. Given their inherent flexibility and compactness, LED strip lights have been instrumental in shaping lighting design concepts around space optimization and creative illuminations.
The Lighting Spectrum: Common Uses and Applications
The utility spectrum of LED strip lights extends beyond traditional domestic settings into realms such as commercial establishments, event décor, DIY projects, and landscape lighting. Herein lies the charm of these versatile luminaries; they deftly transform mundane spaces into mesmerizing spectacles with their alluring glow.
Landscape strip lights have emerged as an effective tool to highlight architectural features or simply create an enchanting ambience around gardens or patios at nightfall. The use of such lighting options has revolutionized outdoor décor strategies by introducing dynamic color palettes that can enhance visual appeal significantly.
In commercial scenarios – be it illuminating product display units in retail stores, creating dynamic signage, or accentuating key architectural features – LED strip lights enhance visibility while adding a pleasing aesthetic aspect.
Events décor offers another platform to showcase the versatility of these lights. From creating magnificent backdrops to illuminating walkways and instilling a dramatic mood at events – LED strip lights do it all with aplomb.
Consider the artistic realm where these strip lights breathe life into DIY projects, crafts, cosplay designs, and other creative endeavors. The ability to customize their length makes them an ideal lighting solution for artists and makers seeking precision lighting for their projects.
Behind the Glow: How LED Strip Lights Work
Peering behind the bright glow of LED strip lights reveals a fascinating world of physics and engineering. As mentioned earlier, these strips consist primarily of tiny LEDs mounted on a flexible circuit board. These LEDs emit light through a process called electroluminescence – a phenomenon where light is emitted from a material when an electric current or strong electric field is passed through it.
The current supplied by your power source travels along the conductive pathway on the PCB, reaching each LED sequentially. As this electrical current passes through each LED’s semiconductor material, it excites electrons within its atomic structure, causing them to release energy in the form of photons, which we perceive as light.
While traditional incandescent bulbs generate heat (and subsequently light) by heating up a filament until it glows white-hot – an inherently inefficient process – LEDs purely operate on electron movement across semiconductor layers, making them more energy-efficient and less heat-generating. This simple yet ingenious mechanism ensures that each small diode contributes towards creating an overall luminous effect, making LED strip lights an exemplary feat in modern lighting technology.
The Science behind LEDs and Heat
Unraveling the Physics of Light-Emitting Diodes (LEDs)
Understanding LED strip lights, especially regarding heat production, necessitates an appreciation of the underlying physics. These devices operate on a principle known as electroluminescence, a phenomenon first observed in the early 20th century. When an electric current passes through certain materials, they emit light – this is electroluminescence in action.
LEDs are composed of semiconductor materials that are specially designed to produce this effect efficiently. When voltage is applied to an LED strip light, electrons move across the semiconductor and fall into ‘electron holes’. This transition releases energy in the form of photons – particles of light. The color emitted by an LED depends on the energy gap of its semiconductor material.
The reason why LEDs are widely used for landscape lighting and increasingly popular in homes and businesses involves more than just their vibrant colors and flexibility. A critical aspect lies in their ability to convert electricity into light with remarkable efficiency.
The Electroluminescence Process: Converting Energy into Light
A conventional incandescent bulb operates differently; it heats a filament until it glows – a process known as incandescence. Unfortunately, much energy is wasted as heat because only about 10% gets converted into visible light.

Contrastingly, LEDs rely on electroluminescence, resulting in far less wastage and more efficient light production. In fact, close to 90% of electrical energy consumed by an LED is converted directly into light – a significant leap from traditional lighting methods.
This increased efficiency could dramatically reduce global electricity consumption if LEDs became ubiquitous – a goal towards which we’re steaming ahead full force with landscape strip lights illuminating our outdoor spaces beautifully at night without consuming vast amounts of power.
Energy Efficiency: Advancing Beyond Traditional Lighting Methods
Energy efficiency is a salient advantage of LEDs, but it’s not simply about consuming less electricity. LEDs’ exceptional longevity compounds this benefit. An average LED strip light can last for up to 50,000 hours – far outstripping the typical lifespan of an incandescent bulb.
This resilience means less frequent replacements, leading to decreased manufacturing demands and reduced environmental impact. The value proposition is indeed compelling: lower energy bills, less waste, and the convenience of rarely needing to change bulbs.
Moreover, this efficiency extends into how LED landscape lighting impacts the surrounding environment. The minimal heat production significantly reduces fire risks and makes them safer for use in areas where conventional lighting would pose a threat.
Why LEDs Produce Less Heat: A Scientific Revelation
Given the significant differences in how LEDs generate light compared to traditional methods, it’s no surprise they produce less heat. When an electric current passes through an LED strip light’s semiconductor material, almost all of it gets converted into light. Only a small amount is dissipated as heat due to inherent inefficiencies at the atomic level.
However, compared with incandescent or fluorescent lights, which lose around 80-90% of their energy as heat due to their reliance on incandescence or gas excitation processes, respectively, LEDs are much cooler operators. Indeed, these scientific revelations behind why LEDs produce less heat have resulted in more widespread adoption in various applications, including landscape strip lights – transforming spaces with color and vibrancy without high energy costs or unnecessary heating.
Do LED Strip Lights Get Hot?
In this modern age of landscape lighting, one of the most commonly asked questions regarding LEDs, particularly LED strip lights, is “Do they get hot?”. This is a crucial question to address, as understanding heat production and management can greatly influence the lifespan and efficiency of your lights.
The short answer is yes; LED strip lights do get warm but considerably less than traditional incandescent or halogen bulbs. Due to their high energy efficiency, most of the power consumed by LEDs is converted into light with minimal energy wasted as heat.
However, it’s crucial to realize that, just like any other electronic device, some heat generation is inevitable. The heat produced by an LED strip light tends to be so negligible that you can safely touch them even after prolonged use without experiencing discomfort.
This minor heat production highlights one of the many advantages of using LED strip lights in various applications such as landscape lighting. By emitting less heat than conventional bulbs, they reduce potential fire risks while providing optimal lighting.
Fact versus Fiction: Debunking Common Misconceptions
The realm of landscape lighting has been laden with misconceptions and myths that often lead to confusion among consumers. One such prevalent myth about LED strip lights pertains to their alleged high-heat output.
The Truth about LED Strip Lights and Heat Production
In reality, comparing an operational LED strip light with a traditional bulb provides tangible evidence debunking this misconception. An incandescent bulb typically operates at a temperature between 200 and 300 degrees Fahrenheit, while a comparable LED would operate at a significantly lower temperature range between 100 and 120 degrees Fahrenheit. This fact alone illustrates that while LEDs do produce some amount of heat, it’s significantly less than their traditional counterparts.
How Hot Do LED Strip Lights Actually Get?
The exact heat output of an LED strip light can vary based on several factors, but as stated earlier, it is typically around 100-120 degrees Fahrenheit. This temperature is lukewarm to the touch and poses minimal to no risk of injury or burns. It’s important to note that these figures are based on quality LEDs operated under ideal conditions; lower-quality products or overly strenuous operating conditions could potentially result in higher temperatures.
Exploring Factors that Affect Heat Production in LED Strip Lights
While the inherent design and operation of LEDs contribute to their low heat output, other elements also play a significant role in determining the amount of heat these lights produce. Several factors can influence the degree to which an LED strip light heats up while in use.
Length of Use
An essential factor is the length of use. While it’s true that LED strip lights generate less heat than traditional bulbs, longer periods of continuous lighting can cause them to warm up. Understanding this factor allows users to better manage their landscape lighting design by ensuring appropriate intervals between usage.
Quality of the Product
The quality and construction of the strip light itself is another factor that influences heat generation. High-quality LED strip lights are designed with efficient heat dissipation mechanisms, which allow for cooler operation compared to cheaper, inferior models.
Environmental Conditions
Ambient environmental conditions also affect how hot an LED strip light gets during its operation. For instance, LEDs used for landscape lighting purposes may experience warmer operating temperatures during the hotter summer months when compared to cooler winter periods due to increased ambient temperatures.
Dangers associated with Overheating LEDs: A Silent Threat
LED strip lights, while recognized for their efficiency and longevity, are not without their challenges. One such challenge is the potential for overheating. The misconception that LED strip lights do not generate heat can often lead to negligence regarding appropriate installation and usage practices. This oversight could result in the overheating of these lighting devices.
To comprehend the potential hazards associated with overheating LED strip lights, it’s crucial to distinguish between typical operational warmth and excessive heat. During normal operation, high-quality LEDs may get warm but should never become too hot to touch.

However, faulty wiring or continuous usage beyond the recommended duration can result in higher heat levels, posing a risk of burns upon direct contact. Moreover, a concern particularly relevant in landscape lighting applications is fire risk.
Although rare and typically resulting from extremely poor quality products or incorrect installation methods, the risk is non-negligible when dealing with improperly managed LED strip lights. Especially in an outdoor setting where landscape strip lights are often nestled amongst flammable materials such as foliage or wooden structures.
Furthermore, excess heat can also lead to a process known as thermal runaway – a chain reaction where increased temperature leads to further increased temperature until eventual failure of the device occurs. Without proper thermal management measures in place, this issue can be a subtle destroyer of otherwise robust lighting setups.
Consider the environmental implications: inefficient energy conversion resulting from overheated LEDs contributes unnecessary carbon emissions into our atmosphere. Hence, not just an individual problem but contributing towards global ecological concerns for us all to bear.
The Impact on Lifespan and Efficiency: The Dimming Truth
Beyond immediate physical dangers associated with excessive heat generation in LED strip lights lies another concerning impact – reduced lifespan and diminished efficiency of your luminous investment. LEDs are celebrated for their impressive longevity compared to traditional incandescent bulbs or even compact fluorescents.
However, this enviable lifespan is reliant on maintaining optimal working conditions for the LEDs – one aspect of which is appropriate temperature management. Overheating can result in a process known as ‘lumen depreciation’. In simple terms, your LED strip lights will start to lose their brightness over time, far quicker than under normal operating temperatures. This deterioration isn’t just a minor annoyance but can lead to poor visibility if used in crucial areas such as walkways or task lighting setups.
Efficiency, another strong selling point for LEDs, also takes a hit when overheating occurs. An overheated LED strip light requires more power to produce the same amount of light as a well-maintained one. Meaning not only does the quality of your lighting decline, but your energy bills may see an unexpected increase.
Increased heat production reduces the operational life of other components within the LED strip lights. The adhesive used to secure strips in place and even the flexible printed circuit board (PCB) housing the LEDs can suffer premature failure under excessive heat conditions. Thus causing further frustrations and unnecessary expenses for replacement or repair. It’s clear then; proper heat management is not just about safety but preserving both performance and longevity of your lighting investment.
The Art of Equilibrium: Preventing Overheating in LED Strip Lights
The Keystone of Coolness: Proper Installation for Heat Management
The first step towards heat regulation in LED strip lights, including those used in landscape strip lights, begins with proper installation. The artistry of installing LED lights transcends just affixing them to a surface. It involves a careful evaluation of the mounting surface, its conductivity properties, and how it could potentially influence the temperature of the LEDs.
Landscape lighting using LED strips must be installed to allow for good air circulation. This can involve leaving a little space between the light and its mounting surface – a measure that assists in heat dispersion. Furthermore, when installing these landscape strip lights or any form of LED strips, avoid coiling or bunching them up, as this could create hot spots due to limited heat dissipation.
The material onto which the strip is being mounted also plays a crucial role in managing heat. Materials such as metal are excellent conductors and can efficiently absorb and dissipate heat away from your LEDs. As such, utilizing surfaces with better thermal conductivity can significantly help regulate your LED light’s temperature.
To further enhance this process during installation, thermal adhesives can be employed instead of standard tape or glue. They not only provide secure mounting but also facilitate efficient heat transfer from the LED strips to the surface they are attached to.
But what’s important is ensuring that your power supply correlates perfectly with your landscape lighting’s energy requirements or any other type of strip lighting you’re using. An overpowering supply may increase current through your LEDs, leading to overheating.
Cool Running: The Role of Heat Sinks in Maintaining Optimal Temperature
Heat sinks serve as an invaluable ally when it comes to maintaining optimal temperatures for your LED strip lights; they act like an expanse where excess accumulated heat is dissipated. Essentially, they are the master regulators of thermal balance, ensuring your LEDs continue producing brilliant luminescence without overheating.
Heat sinks function on the basis of passive heat exchange. They absorb the heat generated by the LEDs and then disperse it into the surrounding environment. Designed with extended surfaces to increase surface area, they are efficient conductors that encourage rapid heat dispersion, thus keeping your LED strips cool.
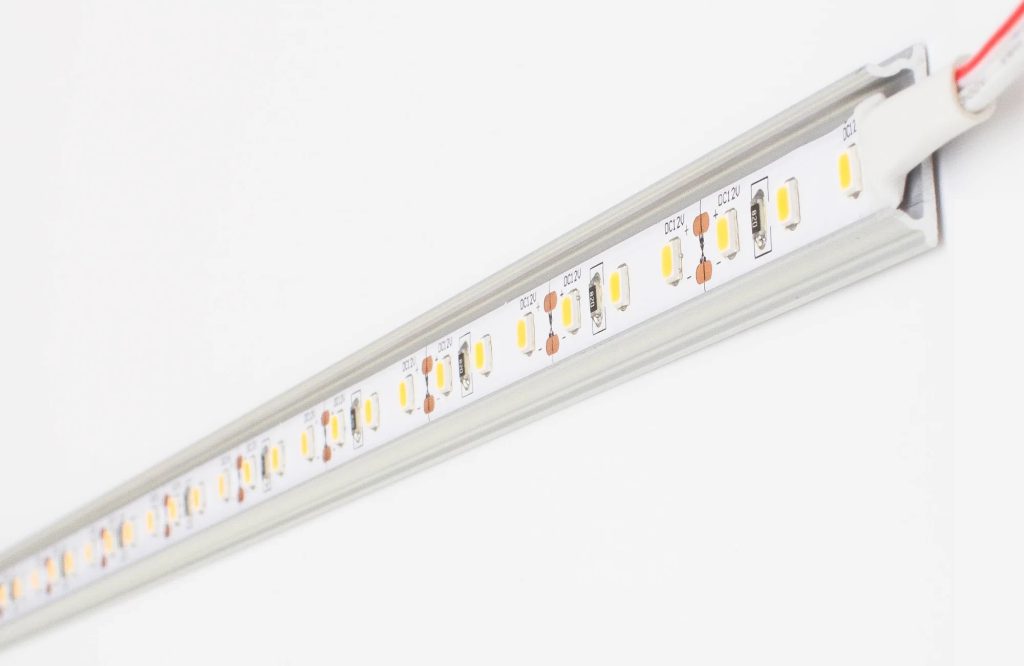

The importance of heat sinks for landscape strip lights or any other form of LED lighting cannot be overstated. They play a pivotal role in maintaining LED lifespan by preventing premature failure due to excessive heat. Therefore, selecting a proper heat sink and ensuring its proper installation are crucial to maintaining optimum performance and longevity of your LED lights.
Aluminum profiles often serve as an integrated solution, offering both mounting services and efficient heat sinking for your strip lights. Their design not only provides a clean aesthetic finish but also ensures improved thermal management.
Bear in mind that not all LED strip light applications will require a heatsink; it depends significantly on factors such as how long they’ll be operated at a time or their brightness level, among others. Nonetheless, for lighting projects that demand prolonged usage, like landscape lighting, incorporation of heatsinks would be judicious.
Mastering Moderation: Tips for Safe Usage to Minimize Overheating
While LED strip lights are lauded for their energy efficiency and minimalistic, sophisticated appeal, particularly in landscape lighting scenarios, safe usage remains paramount to prevent potential overheating issues, which could affect their performance or lifespan.
Firstly, avoid continuously operating your LED strip lights at maximum brightness levels, especially over extended periods; this runs them harder, generating more heat than normal operation does. Preferably use them at brighter settings only when necessary, though even then it should ideally not exceed 90% of their full capacity.
Another effective tip is incorporating breaks into your usage pattern, especially when running them for longer durations, e.g., in landscape lighting. This not only helps extend the useful life of your LEDs but also prevents excessive heat buildup, thereby averting potential overheating.
Keeping your LED strip lights clean is another safety measure you can adopt. Dust and other particulate matter can cover the light and act as a thermal barrier, hindering effective heat dissipation, which could potentially result in overheating.
It’s also wise to regularly examine your LED strip lights for any signs of overheating, such as discoloration, dimming, or flickering, among others. These signs serve as red flags to impending trouble and should not be ignored; immediate corrective measures should be taken once noticed.
Always ensure your LED strip lights are operated within appropriate environmental conditions according to manufacturer guidelines. Extreme temperatures or high humidity levels may impact their performance levels and potentially increase their chances of overheating.
Conclusion: Do LED Strip Lights Get Hot?
The Paramount Importance of Understanding LEDs’ Temperature Dynamics
As we journey into an era where efficient, sustainable, and user-friendly solutions are imperative, understanding the science and mechanics behind products we use daily becomes increasingly important. This is particularly true for LED strip lights due to their ubiquity in various settings, from homes to offices, even extending to landscape lighting.
Exploring whether these LED strip lights get hot not only satiates our curiosity but also equips us with the knowledge necessary for safer deployment and optimal usage. The thermal management of LEDs is a vital aspect that directly impacts their performance, longevity, and safety. A poorly managed LED system can lead to premature failure or even potential hazards. Hence, awareness about the heat generation in LED strip lights offers a roadmap for mitigating potential issues.
Recapitulating Key Findings on Heat Emission from LED Strip Lights
Embarking on our exploration into whether or not LED strip lights get hot led us through an enlightening journey of scientific elucidations and practical implications. We discovered that while LEDs are more energy-efficient than traditional lighting methods by converting most incoming energy into light rather than heat, they indeed generate some level of heat.
However, the temperature at which these LEDs function is significantly lower compared to incandescent or halogen bulbs. We clarified that, contrary to popular belief, it’s not that LEDs do not produce any heat, but rather their innovative design enables efficient heat dissipation, preventing them from getting excessively hot.
Navigating Factors influencing Heat Production in LED Strip Lights
Our exploration further led us deep into factors affecting the degree of heat production by these LEDs. The length of usage emerged as a key influencer whereby prolonged operation could lead to elevated temperatures due to sustained power input.
Also, the quality of the LED strip lights plays a crucial role in heat management. Higher quality products ensure better thermal conductive materials for efficient heat dissipation, thus preventing undue temperature rise.
Environmental conditions also surfaced as a contributing factor. In scenarios like landscape strip lights, where exposure to ambient temperatures can be high, LEDs may exhibit elevated operating temperatures. However, even under these circumstances, LEDs remain safer compared to other lighting alternatives.
Safeguarding against Overheating of LED Strip Lights
We then delved into the dangers posed by overheating of LEDs and underscored the importance of preventative measures. Heat sinks were unveiled as silent heroes helping maintain optimal LED temperatures, thereby extending their lifespan and ensuring sustained efficiency.
Proper installation, too, emerged as a key player in preventing overheating, while tips for safe usage reinforced our armory against potential thermal risks. With this newfound knowledge about LED strip lights and their heat dynamics, we are better equipped to make informed choices and use these versatile lighting solutions optimally and safely.
Appendix: Further Resources for Understanding LEDs and Heat Management
An Abundance of Enlightening Information
Venturing through the realm of LED strip lights, particularly the distinct subject of heat management in these versatile lighting accessories, one might find themselves seeking more authoritative sources. This appendix aims to provide a selection of credible resources that delve deeper into the science behind LEDs, their thermal dynamics, and comprehensive guides about landscape strip lights and landscape lighting.
Towards an Enlightened Understanding
The U.S. Department of Energy provides a wealth of information on the energy efficiency and durability of LED lighting. Their Solid-State Lighting program offers insights on how LED lights generate heat and how this influences their performance over time. Particularly useful is their fact sheet on LEDs and heat management, which gives a detailed explanation about why proper thermal management is crucial for maintaining LED performance, especially for landscape strip lights.
Science Unveiled: The Physics behind LEDs
For those fascinated by the scientific aspects behind LED technology, “The Physics Behind Why LEDs Emit Less Heat” is an article published on The New York Times website. It dives into electroluminescence – the process that makes LEDs glow – without getting too bogged down in complex scientific jargon. It’s an accessible read for anyone interested in understanding why this modern lighting solution has less heat output compared to traditional lighting sources.
Heat Management in Landscape Lighting
A helpful resource specifically aimed at landscape lighting professionals is “Thermal Management in Outdoor Lighting” by Landscape Architect magazine. They provide professional tips on how to manage heat output when designing outdoor spaces with various light sources, including LED strip lights.
Enhancing Aesthetics with Landscape Strip Lights: Safety Precautions
“LED Strip Lights Installation Guide – Safety Tips & Troubleshooting” by Lighting EVER provides an extensive guide on how to safely install and use LED strip lights. They outline the importance of proper heat management in prolonging the lifespan of these lights, especially when they’re used for landscape lighting purposes. This compilation of resources will undoubtedly augment your understanding and guide you towards a fruitful expedition in effective heat management for LED strip lights.
You may also be interested in the following posts:
